What is electricity and how it is made, we have told earlier in this article, in which we have also told that the electricity that is produced is converted to high voltage to move it from one place to another and then it is used at home. Is converted to low voltage. Low voltage electricity cannot be carried away. That is why it is converted to a higher voltage. Apart from this in this post, we will also tell how different transformer are. So let's know what a transformer is and what principle it works on.
What is Transformer
A transformer is a static electrical machine that supplies AC electrical power to another circuit at constant frequency, but the voltage level can be changed, i.e. the voltage can be increased or decreased as needed. Energy transfer is usually accompanied by a change in voltage and current. This decreases or increases the AC current.
This is used to meet a wide variety of needs. Even if the machines in our homes are very high and the current is not enough for us, we make CVT, whose full name is Constant Voltage Transformer. Through this we increase the low voltage as per our wish.
Definition of Transformer
A Transformer may be a stationary device that transfers electricity from one circuit to a different via electromagnetic induction. It's usually wont to increase and reduce the voltage of intensify and step down between circuits.
What principle does the Transformer work on
It works on the principle of Faraday's law of Magnetic Induction according to which
The Magnitude of the voltage is proportional
to the speed of the speed of modification within the flux.
The working principle of the transformer is very simple. When there is a mutual induction between two or more winding which we also know as coil, the electrical energy is transferred between the two circuits.
Suppose you have a winding which we also call coil and in which an AC electrical source is connected, which sends electricity to it. The electricity that flows through this winding produces a constantly changing and alternating flux winding around it. Now here if the second winding is brought closer to this winding, then the smaller portion of alternating flux that is in it connects the second winding to the first winding. Because we know that now the flux is constantly changing its magnitude and direction, so a changing flux must be connected to another winding or coil.
According to the Faraday electromagnetic induction law, an EMF will be indented in the second winding. If the other winding circuit is closed then a current will flow through it. It is the basic working principal of the transformer. The coil or winding which gives the desired output voltage due to mutual induction is normally called secondary winding or coil.
If the Transformer increases the voltage between the primary and secondary winding, we know it as a step up transformer. Conversely, which reduces the voltage between the transfer primary to secondary winding, we know it as a step-down transformer. We will learn more about step-up and step-down transformer in further detail.
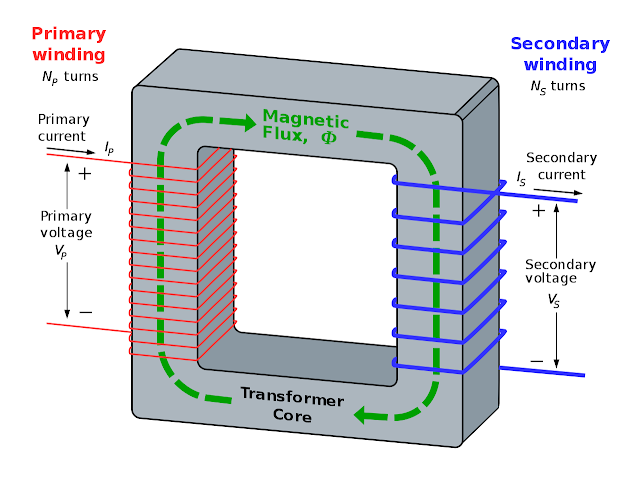
Diagram of Transformer
Practically this is not possible when we talk about an ideal transformer because a very small amount of flux is produced when the primary coil is connected to the secondary coil in open air. Therefore, when the current flows in a closed circuit, which is connected to the secondary winding, it will be very low which cannot be measured.
The rate of change in the flux linkage depends on the amount of link flux of the secondary winding, so ideally almost the primary winding should be linked to the entire secondary winding. A core type transformer is used to effectively and efficiently. This allows low reluctance path flow for both windings to occur. Due to low reluctance, primary winding produces the maximum amount of flux that the link passes in secondary winding. When the Transformer is on and the current is passed, the transformer is known as inrush current.
What are the parts of Transformer?
It Mainly consists of three parts.
- Primary winding
- Magnetic core
- Secondary winding
Primary winding:-
Primary winding is the winding that is connected to the AC current is power source and produces magnetic flux.
Magnetic core:-
The Primary winding that produces magnetic flux goes through this low reluctance link pass to the secondary winding and produces a closed magnetic circuit.
Secondary winding:-
The Flux, produced by primary winding, passes through the core and connects it to the secondary winding. Secondary winding is also connected to the core and allows us to create the output voltage as desired.
Importance of Transformer
If you go to any city or village, if there is electricity there will definitely be a transformer because without it the homes of the current people cannot be reached. It is planted everywhere according to the population. According to its capacity, electricity is given to as many houses as it can handle. The higher the capacity of the transformer, the more power it can supply to the households. When the load is high, the voltage decreases and people have to face troubles.
It has a lot of importance in our life because whenever we have a transformer in your area, if it gets burnt, then we have to live in darkness without electricity and even the machines that run from it get stalled.
- Usually electrical power is generated in 11 kilo volts.
- For economic reason, a very high voltage is converted to 220 kV or 440 kV for sending AC power for long distances. That is why step up transformer is used to convert the power generated in the power station to high voltage.
- For safety reasons, the voltage is changed at all stations with the help of step-down transformers.
- So that they can be sent and used in different places, the voltage is changed to 400/230 V from the step-down transformer.
What is the efficiency of Transformer
The efficiency of the transformer is 90-98%. Its efficiency is always between 0 and 100% but it can never be 1% or 100%.
What is the type of Transformer?
Types based on core and winding positions
Core type
Core type transformers are transformers in which primary winding and secondary winding are placed around each limb. There is a core type and there is a magnetic circuit which is equivalent to an electric series circuit. Lamination is in the form of E and L strip. It requires more copper. This winding is also known as Concentric Winding and cylindrical Winding. It consists of 2 limb.
Shell type
In shell type transformers, two windings are placed in the center core. Shell type core is equivalent to electric panel circuit. Lamination is in the form of L strip. It requires less copper. This winding is also known as Sandwich and Disc winding. It consists of three limb.
Types based on Winding
1. Step-up Transformer:-
When the voltage is increased on the outside, the transformer is called a step-up transformer, in which the number of turns means that the number of copper wires wrapped on the coil is more than the secondary winding. Because its secondary side high voltage is developed.
In countries such as India, power is usually generated at 11Kv. Step up transformers are used to send very high voltage over long distances due to economical reasons. The power created for this is first sent to the power station and then with the help of step-up transformer, the voltage is converted to high voltage (220v-440v) and then it is transported over a long distance.
2. Step-down Transformer:-
A step-down transformer reduces the output voltage or, in other words, converts high voltage low current power to a low voltage high current power. To deliver power to different regions, the voltage has to be changed to 440v / 230v for safety reasons and step-down transformer is used for this. In this way, secondary winding has no compared to primary winding. of turns is low due to which the voltage can be reduced.
Types on service basis
1. Power Transformer:-
A Power Transformer is a transformer that is used to transfer electrical energy to any part of an electrical and electronic circuit and is between a generator and a distribution and primary circuit. There are many types of small power transformers such as medium-sized power transformers.
2. Distribution Transformer:-
Distribution A transformer is a transformer that is used to transfer electrical energy to any part of an electrical and electronic circuit and is between a generator and a distribution and primary circuit. These transformers are used for distribution system interface. Liquid is used in a common power transformer and has a lifespan of about 30 years. There are also many types of power transformers such as small power transformers medium size and large size power transformers.
- Small Power Transformers can range from 500-7500kVA.
- Medium Power Transformers can range from -100MVA.
- Large Power Transformers can have a range of 100MVA and above.
Instrument Transformer
Instrument Transformers are used to measure electrical quantity in AC systems such as voltage, current, power, energy, power factor, frequency, etc. Instrument Transformers are used as protection layers to protect the power system. The basic function of an instrument transformer is to step-down the voltage and current of the AC system. The voltage and current level of the power system are very high. Instruments that measure very high voltage and current have a very high design cost. Normally measuring instruments are designed to measure current and voltage of 5 amperes and 110 volts.
In this way it is made easy to measure very large electrical quantity scores, that too with the help of instrument transformers. Such instrument transformers are quite popular in modern power systems.
Current Transformer
Current Transformer is a type of instrument transformer. Its design is designed to produce alternating current in secondary winding which is proportional to the current measured in primary winding. Current transformers convert high voltage current to a very small amount and provide an actuating electrical current flow in the AC transmission line with safety. Extended ammeter is used for this.
Potential Transformer
A Potential Transformer is a voltage step-down transformer that lowers the voltage of a high-voltage circuit to measure through low voltage. According to monitoring, they are connected across or parallel lines. Its basic principle of operation and construction is similar to that of standard power transformer.
Auto-Transformer
Auto Transformer is a transformer which has only one winding and which is on the laminated core. It is similar to two winding transformers, the only difference is that the connection between the primary and secondary is different, a part of the winding is common for both primary and secondary. In the load condition, one part of the load current is taken from the supply and the remaining part is taken from its action. It acts as a voltage regulator.
In short
In Today's post, you have learned what a transformer is. Transformer is the most important role that we get 24 hours a day. When the transformer installed around the house goes bad, there is chaos between people. If seen, it has become a very important part of our life, now whether people live in cities or in villages, it is the same. That is why you must have understood what it means in our life.
Through this post you also learned on what principle the transformer works and what is its type. What is its definition and what rules does it work on. We have also given you information through the article about what its parts are. I hope you enjoy this post. If you find this post helpful, then share it with friends in Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and WhatsApp.

















0 Comments